What Is a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic management tool used to evaluate and enhance various internal business functions and their resulting external outcomes. It serves as a performance metric that offers valuable insights for organizations to make informed decisions. Widely adopted in countries like the USA, UK, Japan, and Europe, Balanced Scorecards require rigorous data collection to provide quantitative results. This information empowers company personnel to improve future strategies.
Key Takeaways
- A Balanced Scorecard is a performance metric that identifies and enhances a business’s functions and outcomes.
- Introduced in 1992 by David Norton and Robert Kaplan, it incorporates nonfinancial information for a holistic view.
- Originally for-profit focused, BSCs have been adapted for nonprofits and government agencies.
- The model includes four key areas: Learning and growth, business processes, customers, and finance.
- Provides comprehensive insights beyond financial performance to drive organizational efficiency.
Investopedia / Michela Buttignol
Understanding Balanced Scorecards (BSCs)
The Balanced Scorecard was introduced by Dr. Robert Kaplan and Dr. David Norton in 1992. Initially developed for profit-driven entities, it evolved to serve nonprofits and government bodies. This tool measures a company’s intellectual capital, encompassing skills, knowledge, and unique advantages that shape competitiveness in the market.
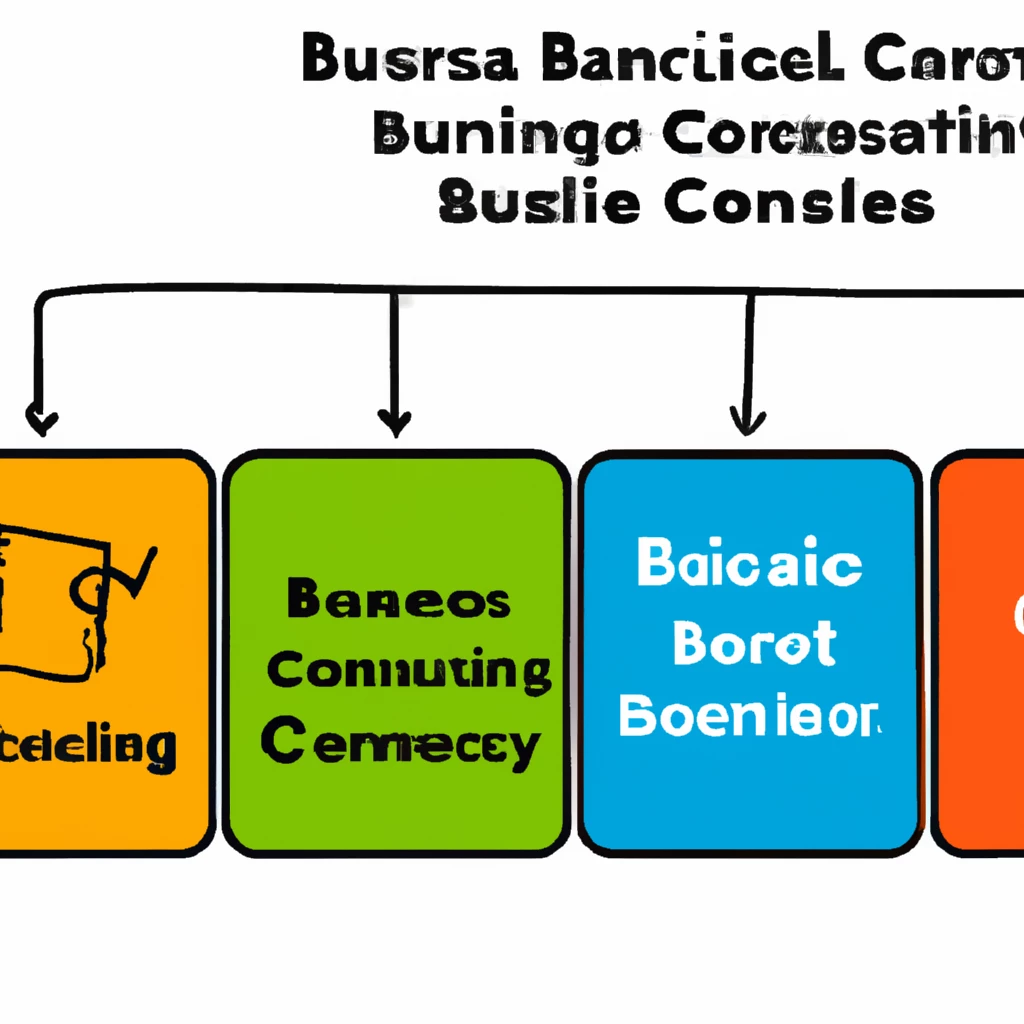
The BSC model focuses on four critical areas, known as legs, including learning and growth, business processes, customers, and finance. By analyzing these facets, companies gain actionable insights to drive strategic initiatives and enhance bottom-line performance.
The Balanced Scorecard supports organizations in implementing strategy mapping to pinpoint value creation areas and streamline operations for improved efficiencies.
Characteristics of the Balanced Scorecard Model (BSC)
The Balanced Scorecard collects data from four core aspects of a business:
- Learning and growth: Evaluates training and knowledge resources to drive competitive advantage.
- Business processes: Assesses operational efficiency for product manufacturing.
- Customer perspectives: Gauges customer satisfaction and feedback on products and services.
- Financial data: Examines financial performance metrics such as sales, expenditures, and income.
Active management is required to analyze the data collected across these four areas, reinforcing the organization’s vision and strategy.
The Balanced Scorecard is primarily a management tool, aiding key personnel in driving organizational success through strategic analysis.
Benefits of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Balanced Scorecards offer numerous advantages, consolidating information into a single comprehensive report for efficient decision-making. This streamlined approach saves time and resources, facilitating operational improvements.
Additionally, BSCs provide insights into service quality, aiding in stakeholder communication and goal alignment. By identifying and addressing inefficiencies, organizations enhance productivity and mitigate risks.
Examples of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Companies utilize internal or external BSC evaluations to gauge performance. From customer service surveys to services by firms like J.D. Power, these assessments identify strengths and weaknesses for strategic improvement.
Balanced Scorecard (BSC) FAQs
What Is a Balanced Scorecard and How Does It Work? A Balanced Scorecard is a management tool that evaluates internal operations to improve external outcomes, guiding future decisions based on past performance data.
What Are the Four Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard? The four perspectives include learning and growth, business processes, customer perspectives, and financial data. These aspects are vital for organizational strategy and require thorough analysis by key personnel.
How Do You Use a Balanced Scorecard? Balanced Scorecards integrate intellectual and financial data to unravel internal successes and shortcomings. Through data consolidation and analysis, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies and communicate goals effectively.
What Are the Balanced Scorecard Benefits? Balanced Scorecards offer advantages such as streamlined reporting, holistic performance tracking, and efficiency improvements. They help companies recognize and rectify operational inefficiencies for enhanced performance.
What Is a Balanced Scorecard Example? Companies leverage internal assessments or external firms like J.D. Power for evaluation. These methods aid in identifying areas for improvement in products and services to drive organizational success.
The Bottom Line
Balanced Scorecards empower companies to streamline their internal processes for enhanced financial performance. By focusing on learning and growth, business processes, customers, and finance, organizations can efficiently drive improvements, align stakeholders, and bolster their market position.